Typical red-tape: a tax number alone is not enough. No, there is a second number: the sales tax ID. Who else should know about this?
- In this article you will learn: *
- How the sales tax ID and tax number differ
- When which number is used on your invoices
- Where and how you can apply for the two numbers
Tax number or VAT ID: Which number must be on the invoice?
One, neither or both? That is the big question that we want to answer at this point.
In principle, both the tax number and the sales tax ID serve to identify a company for tax purposes. An invoice without an identification number is therefore not permitted - you must specify one of these two numbers:
- Tax number / tax ID
- Tax ID
Tax number or VAT ID: Which number must be on the invoice?
One, neither or both? That is the big question that we want to answer at this point.
In principle, both the tax number and the sales tax ID are used to identify a company for tax purposes. An invoice without an identification number is therefore not permitted - you must absolutely specify one of these two numbers:
- Tax number / tax ID
- Tax ID
Tax number: The tax number on invoices within Germany
If you issue invoices to people or companies that have their headquarters in Germany like you do, it is generally sufficient to state the tax number or tax ID on the invoice. You can recognize them by their 11-digit structure: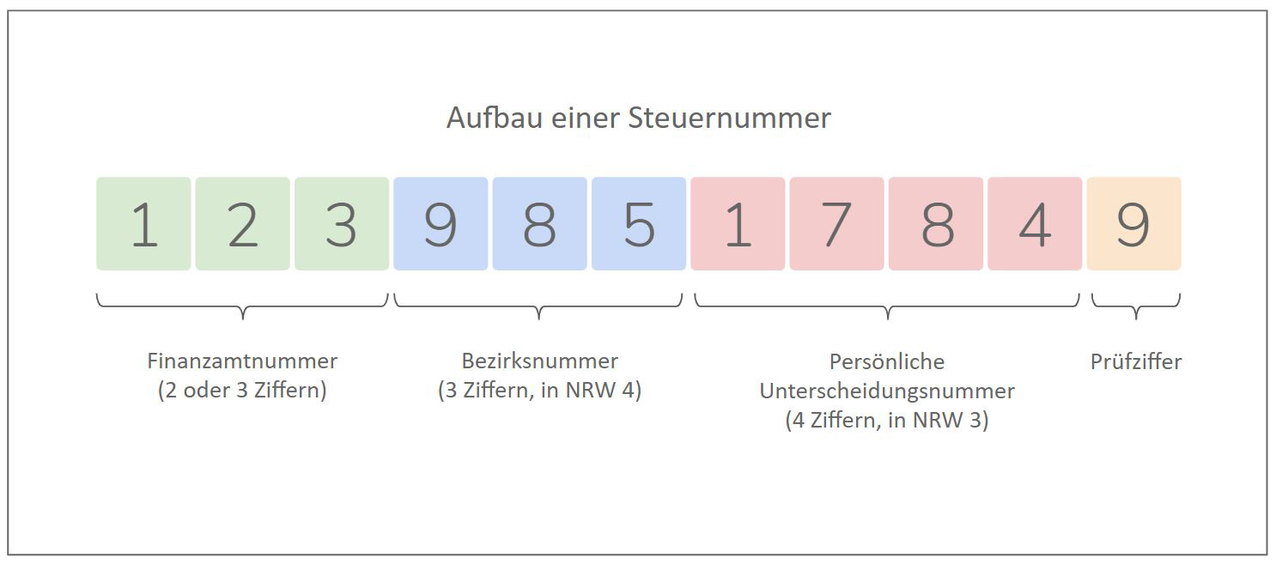 If your customer is based in Germany, according to § 14 UStG, you can also enter your sales tax identification number (sales tax ID) instead of the tax number.
If your customer is based in Germany, according to § 14 UStG, you can also enter your sales tax identification number (sales tax ID) instead of the tax number.
Many entrepreneurs even prefer to give their VAT ID voluntarily. It is more secure in terms of data protection and offers fewer opportunities for abuse than the tax number.
Sales tax ID: The tax number on invoices to other EU countries
For invoices that you send to customers in other EU countries, you need the VAT identification number in certain cases.
Sales tax ID for B2B businesses
The sales tax ID is mandatory if you, as a regular entrepreneur subject to VAT, write an invoice to another regular entrepreneur in other EU countries (B2B business).
Because then it is an intra-community delivery or service or the reverse charge procedure. You can find out how to use the reverse charge procedure specifically in our article Invoice EU abroad without sales tax
Note that in this case you are not allowed to charge sales tax. Your invoice is therefore VAT-free. For this, the invoice should include your own VAT ID as well as that of the invoice recipient.
You can recognize the VAT ID by its structure of 11 digits and the country code in front of it. As an entrepreneur in Germany, you have the abbreviation DE in your VAT ID: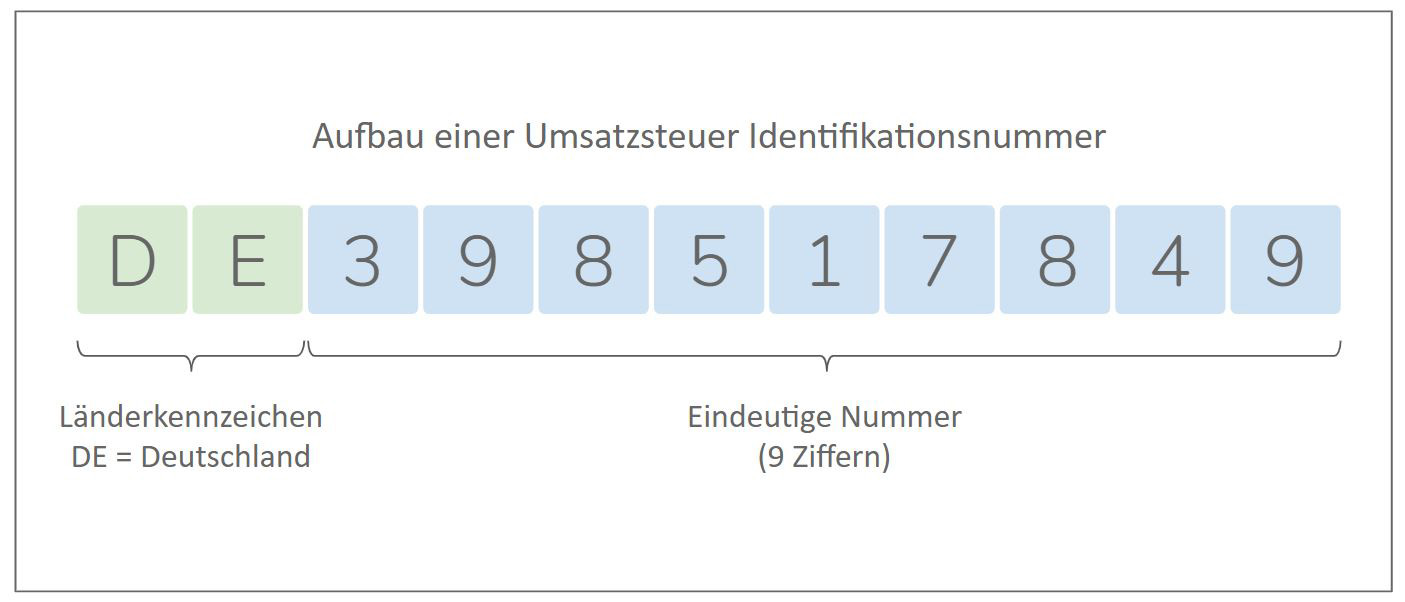
No sales tax ID for all other businesses
If, on the other hand, you are a small business owner or your customer in another EU country is a private person or small business owner, nothing will change for you.
You issue a very regular invoice - just like you always do: As a regular entrepreneur, you write an invoice with sales tax, as a small business owner a small business invoice without sales tax. In this case, you do not need a VAT ID.
Tax number + VAT ID = well prepared!
Our tip: It can't hurt to have both numbers, i.e. both the tax number and the sales tax identification number. If a customer prefers a certain number, you are perfectly equipped.
Importance of sales tax ID and tax number for companies
But what exactly do the numbers mean? Both are long and cumbersome. Find out why you need a tax number and how it differs from the sales tax identification number. Here's what you should know:
What are the tax numbers and sales tax IDs for?
The tax number is the number under which tax matters of a natural or legal person in Germany are kept at the tax office.
The VAT identification number is used to identify entrepreneurs and legal entities subject to VAT in the European Union (EU) who are active on the European single market across borders.
Tax number on invoices under 250 euros?
No! There is no need for a tax number on invoices under EUR 250. Such so-called small amount invoices are e.g. Train tickets, fuel receipts, or receipts. You can find out more about this in our article on small amount invoicing.
-1.png?height=120&name=Consultinghouse-Market-Entry-Germany%20(1)-1.png)